Understanding Mobile Operating Systems: iOS, Android, Custom OS, and HarmonyOS Explained
Discover the key differences between iOS, Android, custom Android OS versions, and HarmonyOS (including HarmonyOS NEXT). Learn how mobile OS choices affect apps, updates, and developer tools.
What is a Mobile Operating System (OS)?
If you've ever wondered what really powers your smartphone, you're in the right place. A Mobile Operating System (OS) is the brain behind your device — it runs everything from the apps you use to how the screen responds to your touch.
There are two major players in the mobile OS world:
- iOS – found only on Apple devices like iPhones and iPads.
- Android – used by a wide range of brands including Samsung, Xiaomi, OPPO, OnePlus, and more.
Now, here’s where it gets interesting: Apple keeps iOS locked down and consistent, while Android is open-source. That openness gives manufacturers the freedom to tweak, customize, and brand Android in their own way. Let’s unpack both ecosystems.
Exploring the iOS Ecosystem
iOS is Apple’s tightly integrated mobile OS — designed to work hand-in-hand with Apple’s hardware.
Because of this, iOS offers a polished, uniform experience across all supported devices. Updates roll out quickly and consistently. You’ll never see iOS running on a non-Apple device — it’s a closed system, and Apple likes to keep it that way.
This setup means fewer surprises, better optimization, and stronger security. But it also means less flexibility and customization compared to Android.
Let’s Explore the Android Ecosystem
Now let’s talk Android. Android is like a set of tools from Google that phone brands can use to build their own versions. That’s why Android looks and feels different depending on which brand you’re using.
Ever checked your phone settings and seen both “Android Version” and “OS Version”? Here’s what they mean:
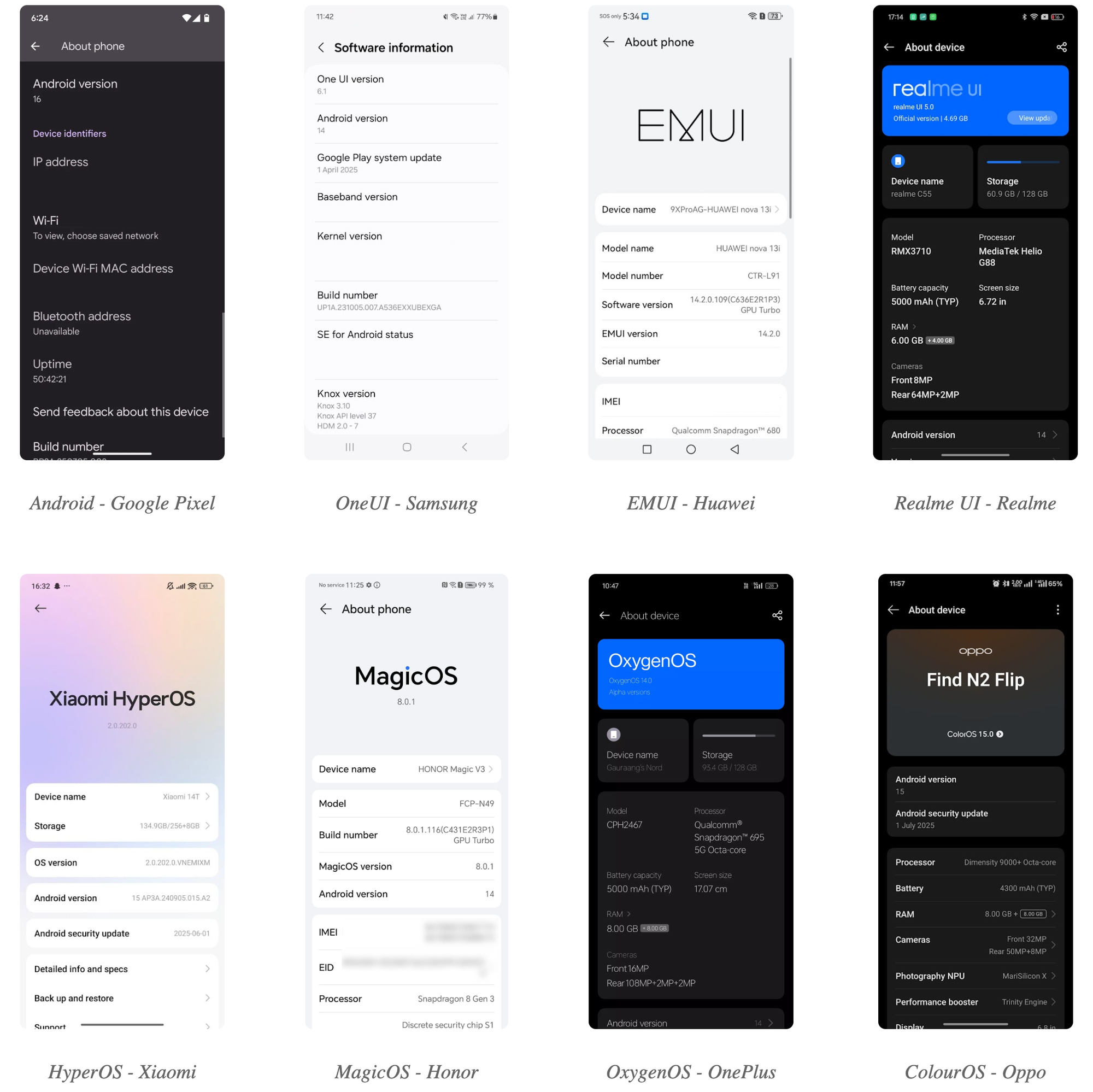
🔹 Android Version
This refers to the core system developed by Google — like Android 13, 14, 15 or 16. It determines major features, app compatibility, security updates, and developer tools.
Phones like the Google Pixel often run a version of Android that’s close to Google’s original design. But even Pixel phones add a bit of their own flavor — animations, exclusive features, and UI tweaks.
📝 Some phones, like the Xiaomi Mi A3, launched with stock Android (no custom UI), but that’s getting rare these days.
🔹 OS Version (a.k.a. Custom UI)
This is the brand’s personal spin on Android. Think Samsung’s One UI, Xiaomi’s HyperOS, or OPPO’s ColorOS.
These custom UIs change the look and feel of Android — menus, icons, built-in apps, and extra features. But under the hood? It’s still Android doing the heavy lifting.
So even if your phone says “HyperOS” or “EMUI,” it’s not a different operating system — it’s Android with a custom outfit.
Why Android Version Matters (More Than You Think)
One important thing to understand — especially as a developer or informed user — is that the Android version matters far more than the custom UI version when it comes to:
- App compatibility
- Feature availability
- Security standards
- API behavior
That’s why app developers care more about whether you’re running Android 13 than whether you’re using One UI or HyperOS.
And for users, a newer Android version means your phone can do more — and stay safer — for longer.
OS Update Lifespan — Brand by Brand
Not all phone brands treat software updates equally. Some go the extra mile to keep your device current, while others move on a bit faster.
Here’s a quick look at how long major brands support their phones:
| Brand | OS Update Duration | Security Patch Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Google Pixel | 7 years (Pixel 8 and newer) | 7 years |
| Samsung | 4–5 years (varies by model) | 5 years |
| Xiaomi | 2–4 years (flagship gets longer) | 3–5 years (for major devices) |
| Huawei | Typically 2 years (HarmonyOS-based) | 2–3 years |
| OPPO | 2–4 years (flagship receives more) | 3–4 years |
| OnePlus | 3–4 years (flagship), 2–3 years (mid-range) | 4 years (flagship) |
| Apple (iPhone) | 6–7 years | 6–7 years |
HarmonyOS vs. HarmonyOS NEXT — What’s the Difference?
If you’ve been following Huawei, you might’ve heard of HarmonyOS and HarmonyOS NEXT.

🔹 HarmonyOS (Original)
Huawei’s first version of HarmonyOS still relied heavily on Android. It could run Android apps and shared some core components with it. In short, it was more of a modified Android system with Huawei’s branding.
Mean HarmonyOS still supports APK files. Apps built using Android Native, Flutter, or React Native can be installed as long as they are packaged as APKs.
🔹 HarmonyOS NEXT
This is a whole new chapter. HarmonyOS NEXT:
- Doesn’t support Android apps
- Has its own SDK (software tools for developers)
- Is built from the ground up by Huawei
HarmonyOS NEXT, does not support APKs. Apps must be built specifically for it using DevEco Studio, with development done in ArkTS (an enhanced version of TypeScript), using ArkUI and the Ark Compiler.
Apps must be built specifically for it using DevEco Studio, with development done in ArkTS.
Developers have to build apps specifically for this new platform. It’s Huawei’s bold step away from the Android world.
App Distribution Platforms: Play Store, App Store & AppGallery
Every ecosystem needs a place to get apps. Here’s how the big three stack up:
| Store | Used By | Platform Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Play Store | Samsung, Xiaomi, OPPO, OnePlus, Pixel, etc. |
Android (AOSP-based) | Official Android marketplace managed by Google. |
| Apple App Store | Apple (iPhone, iPad) | iOS only | Strictly curated and controlled by Apple. |
| Huawei AppGallery | Huawei (HarmonyOS / HarmonyOS NEXT) |
Android-compatible (HarmonyOS), Native-only (HarmonyOS NEXT) |
Huawei’s own app store replacing Google Play on its devices. |
Final Thoughts
Most users don’t notice the differences between iOS, Android, and custom Android OSes—because day to day, things just work. But for developers, tech enthusiasts, or anyone curious about how smartphones truly operate, these differences matter.
Understanding how each mobile OS handles apps, updates, and customization can help you make smarter choices when buying a phone or building apps.
Hopefully, you’ve learned something new here—and gained a deeper appreciation for the OS running in your pocket.

